If you’re curious about what DDoS is and how it impacts the performance of a website, this article is for you! DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) is one of the most common cybercrimes, where an attacker floods a server with fake internet traffic, preventing users from accessing the website’s online services. These attacks can have various motives, such as revenge, financial harm, extortion, and more. Even the largest global companies are not immune to such attacks. In the following, we will discuss in detail what DDoS is, how it works, and its impact. Stay with us.
What is DDoS?
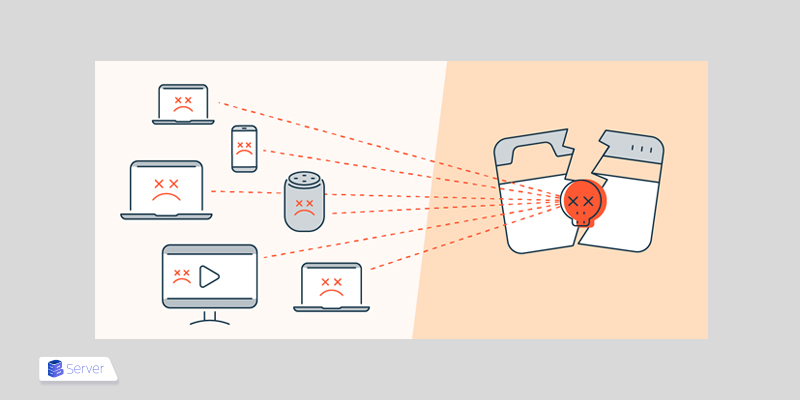
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks are a subclass of Denial of Service (DoS) attacks. In DDoS attacks, multiple online devices, known as a botnet, connect together and generate fake traffic aimed at a specific website.
Now that you have a general understanding of what DDoS is, you’ve likely realized that these attacks, unlike other cyberattacks, do not cause vulnerabilities in your website’s security environment. Instead, the goal of DDoS attacks is to make your website inaccessible to legitimate users.
DDoS attacks affect the entire online user base and can occur in short bursts or be repeated frequently. In either case, these attacks will have significant negative impacts on your website or business, which may last for days, weeks, or even months. DDoS attacks can lead to loss of revenue, long-term damage, decreased consumer trust, and incur additional costs. These attacks can even pose risks to websites that are hosted and operated on VPS.
Now that you fully understand what DDoS is, it’s time to dive deeper into how it works.
How Do DDoS Attacks Work?
DDoS attacks are carried out using a network of internet-connected machines. In other words, a group of computers and other devices (such as IoT devices) that have been infected with malware (a botnet) are controlled remotely by an attacker. To better understand what DDoS is and how it works, you can think of these devices as a group of zombies attacking a website and taking it offline.
Each of these devices sends requests to the targeted IP address, overwhelming the network and preventing normal traffic from going through. Since these bots are legitimate internet devices, it is extremely difficult to distinguish attack traffic from regular traffic.
One of the best practices to counter such attacks is to always keep your system and Windows vps up to date and manually configure network rules.
How to Detect a DDoS Attack
You may be wondering, what are the tools used to detect a DDoS attack, and how can we distinguish between these attacks and other cyberattacks?
One of the most prominent signs of a DDoS attack is noticeable slowness in the speed of your website or service, or your website may become completely inaccessible. However, since slowdowns or outages can have various causes, further investigation is required.
One possible solution for detecting these attacks is using website traffic analysis tools. In these tools, you can look for the following:
- A large volume of suspicious traffic coming from a single IP address or IP range.
- High traffic from users with similar behavioral patterns (such as device type, location, or browser version).
- An increase in requests for visiting a specific page or service.
- Unusual behavioral patterns, such as a surge in visits at a specific time of day or repeated visits within a set time period (for example, every 10 minutes).
- In addition to the above, there are other signs of these attacks that may vary depending on the type of attack.
To detect the number of connections to the web server port and suspicious IPs on a Linux VPS, you can use certain commands to identify high numbers of connections coming from specific IP addresses and block them.
What Are the Most Common Types of DDoS Attacks?
Now, let’s explore the different types of DDoS attacks and how we can categorize them.
To understand how these attacks work, we first need to talk a bit about network connections. A network connection over the internet is made up of 7 distinct layers, each with a different purpose. These layers, in order, are:
- Physical Layer
- Data Link Layer
- Network Layer
- Transport Layer
- Session Layer
- Presentation Layer
- Application Layer
In general, DDoS attacks can be divided into two main categories:
Infrastructure Layer Attacks (Known as Layer 3 and 4 Attacks)
Layer 3 and 4 attacks are commonly known as infrastructure layer attacks. These are the most common types of DDoS attacks and include SYN floods and other reflective attacks, such as UDP floods. The volume of infrastructure layer attacks is usually high, and their goal is to overload the capacity of servers or the network. Fortunately, due to the clear signature of these attacks, they are easier to detect, allowing you to resolve the issues and restart your website in the shortest possible time.
Application Layer Attacks
Application layer attacks occur at layers 6 and 7 of the network. These attacks are less common than infrastructure layer attacks but are more complex and, as a result, harder to detect.
Compared to infrastructure layer attacks, application layer attacks are smaller in volume and typically focus on more resource-intensive parts of the application. For example, HTTP request floods to a login page, or a costly search API, or WordPress XML-RPC floods (commonly known as pingback attacks) are considered application layer attacks.
How to Prevent DDoS Attacks?
DDoS attacks can derail the success of a business and cause significant damage. But is it possible to combat them? What are the ways to prevent DDoS attacks, and how can these solutions be implemented?
The good news is that there are many strategies available to defend against these types of attacks. Some of the most important strategies to prevent DDoS attacks include:
Attack Mitigation
One of the first and simplest techniques to mitigate DDoS attacks is to minimize the level at which the attack can occur. By implementing this strategy, attackers have fewer options to exploit. To achieve this, you can place your computing resources behind Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) or Load Balancers, and also restrict direct traffic to specific parts of your website’s infrastructure, such as database servers. Using firewalls or Access Control Lists (ACLs) to manage application traffic is another technique that you can implement.
Scalability Enhancement
To reduce the impact of such attacks, you can use two excellent strategies:
Increase Bandwidth Capacity: When designing your applications, make sure your hosting provider offers ample redundant internet connections. This feature allows you to handle large volumes of traffic.
Increase Server Capacity: Most DDoS attacks consume large amounts of resources. Therefore, it’s important to be able to scale your computational resources up or down immediately after an attack.
Understand the Difference Between Normal and Abnormal Traffic
You need to be able to recognize the amount of traffic hitting your host and understand how much traffic the host can handle without going offline. This concept is called “rate limiting.” More advanced protective techniques work intelligently by only accepting traffic that matches their analysis. To do this, you must understand the characteristics of legitimate traffic that is typically targeted and be able to compare each packet with those characteristics.
Deploy a Firewall
One effective solution is to use a Web Application Firewall (WAF). This firewall protects your website against attacks such as SQL injection or cross-site request forgery.
Risk Assessment
It’s important to be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of your software and hardware assets, and prepare strategies to mitigate potential damage. By doing this, you can manage the damage and minimize the impact quickly in the event of an attack, without wasting time.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DDoS attacks are a growing threat to online businesses and services, capable of causing significant damage by overwhelming websites with fake traffic. Understanding how these attacks work and being able to detect and mitigate them is crucial for maintaining a secure online presence. By implementing the right strategies, such as enhancing scalability, using firewalls, and employing DDoS protection tools, you can significantly reduce the impact of these attacks. Remember, proactive measures and timely responses are key to keeping your website safe from DDoS disruptions.
FAQs
What are cloud-based DDoS protection solutions, and are they more effective than other measures?
A common argument made by cloud service providers is that large-scale DDoS attacks affect local resources before they are detected. Therefore, instead of relying on local detection systems, it’s better to route traffic through a cloud-based protective service that filters malicious traffic before it enters the network.
In response to this claim, it’s true that cloud services are beneficial against DDoS attacks, but not all traffic should be routed through these services. Doing so would increase costs and create delays.
Can ISPs protect websites from DDoS attacks?
ISPs act as internet gateways and can be useful in defending against DDoS threats. However, due to the massive volume of malicious traffic and the increasing complexity of DDoS attacks in recent years, ISPs alone are not enough to protect a website effectively.
What are the differences between DoS and DDoS?
Most people immediately think of DDoS when they hear “Denial of Service.” While this isn’t entirely wrong, there’s a difference. DoS stands for Denial of Service and refers to a category of cyberattacks that includes a wide range of techniques, including DDoS or Distributed Denial of Service attacks. A DDoS attack is a type of DoS attack that originates from multiple sources and is spread across different locations.