If you are looking to manage your team projects in a professional, precise, and well-coordinated manner, installing Jira on your server can be one of the best choices. Jira is a powerful software solution for task tracking, workflow management, and team collaboration, and by deploying it on your own server, you gain full control over all its capabilities. This guide also outlines essential Jira installation steps to help you complete the setup smoothly.
In this tutorial from Buyserver Magazine, we will walk you through the complete process of Jira setup on a Linux server. All steps follow recommended best practices, and you can perform them using either a Linux VPS or a dedicated server.
What Is Jira?
Jira is one of the popular products developed by Atlassian, designed for project management, task tracking, and automating structured workflows across teams. This software enables teams to closely monitor progress and task status from the beginning of a project to its completion. Jira can be used across various departments, including software development, human resources, marketing, support, and even operational units.
In Jira, every activity is defined as an Issue, representing a software bug, a support request, an idea, or even a simple task.
A collection of these tasks is organized into a Project, and each project has its own workflow. Workflows visually map the progress of tasks and are commonly based on Kanban or Scrum methodologies. Each workflow can be fully customized—from the moment work begins until it reaches completion.
Jira is available in two modes: a cloud-based service hosted by Atlassian, or a self-hosted deployment on your own server, which is the focus of this guide. To install Jira, you will need proper hardware and software resources; if you lack dedicated hardware, a well-configured VPS is sufficient.
Originally created for bug tracking and issue management, Jira has evolved—through expansions and add-ons—into a comprehensive tool supporting Agile teams, DevOps pipelines, and complex software projects.
What Are the Uses of Jira?
Some key applications of Jira include:
- Task Management: Creating, dividing, prioritizing, and tracking tasks using Kanban or Scrum boards.
- Software Project Management: Coordinating development, QA, and management teams across the software lifecycle.
- Bug Tracking: Logging bugs, assigning them to team members, and monitoring their resolution.
Agile Team Management: Supporting Scrum and Kanban with features like backlogs and sprints. - Advanced Reporting: Providing visual reports on project status, team performance, and key metrics.
Benefits of Using Jira
Jira is not just a task-tracking tool; it is a powerful platform for aligning teams with organizational goals. Some of its standout benefits include:
- High Customizability: Full control over fields, workflows, and issue types.
- Integration: Seamless compatibility with GitHub, Confluence, Bitbucket, Jenkins, and more.
- Scalability: Suitable for both small teams and large enterprises.
- Enterprise-grade Security: Features authentication, SSO, encryption, and granular permissions.
- Flexible Access: Available both as a cloud platform or as a self-hosted solution for full control.
Prerequisites for Installing Jira
Before you begin, ensure your server meets the requirements needed for a stable Jira installation Linux environment.
| Prerequisite | Description |
| Operating System | Linux (recommended: Ubuntu 20.04 or CentOS 7/8) |
| Java | Java 8 or 11 (JDK or SDK) |
| Database | PostgreSQL 12/13, MySQL 5.7/8.0, Oracle, or MS SQL |
| Root Access | Required for setup |
| Disk Space | Minimum 10 GB free |
| RAM | Minimum 2 GB (recommended: 4 GB+) |
| Ports | Port 8080 for web access |
| Internet | Stable connection for downloads |
Installing Jira on Ubuntu
In this section, we walk through how to install Jira on Ubuntu 24.04 step by step.
- Note 1: Users should be familiar with SSH.
- Note 2: At least 4 GB RAM is recommended.
Step 1: Install MySQL Server and Create the Database
Install MySQL and required packages:
apt-get install mysql-server unzip fontconfig -y
Access the MySQL shell:
mysql
Create the Jira database:
CREATE DATABASE jiradb CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_bin; CREATE USER 'jirauser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password'; GRANT ALL ON jiradb.* TO 'jirauser'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; EXIT;
Step 2: Download and Install Jira
Visit the official Jira Software website and download the installer:
wget https://www.atlassian.com/software/jira/downloads/binary/atlassian-jira-software-10.3.6-x64.bin
Make the installer executable:
chmod a+x atlassian-jira-software-10.3.6-x64.bin
Run installation:
./atlassian-jira-software-10.3.6-x64.bin
You will be prompted to configure:
- Installation type: Express or Custom
- Installation directory (default: /opt/atlassian/jira)
- Auto-start options
- HTTP port (8080) and RMI port (8005)
Verify Jira is running:
ss -antpl | grep java
Sample output:
LISTEN 0 1 [::ffff:127.0.0.1]:8005 ... LISTEN 0 100 *:8080 ...
Step 3: Configure the JDBC Driver
Download MySQL JDBC driver:
To allow Jira to connect to MySQL, you must download the MySQL JDBC driver and move it to the Jira directory:
wget https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/Connector-J/mysql-connector-java-8.0.18.zip unzip mysql-connector-java-8.0.18.zip cp mysql-connector-java-8.0.18/mysql-connector-java-8.0.18.jar /opt/atlassian/jira/lib
Restart Jira:
/etc/init.d/jira stop /etc/init.d/jira start
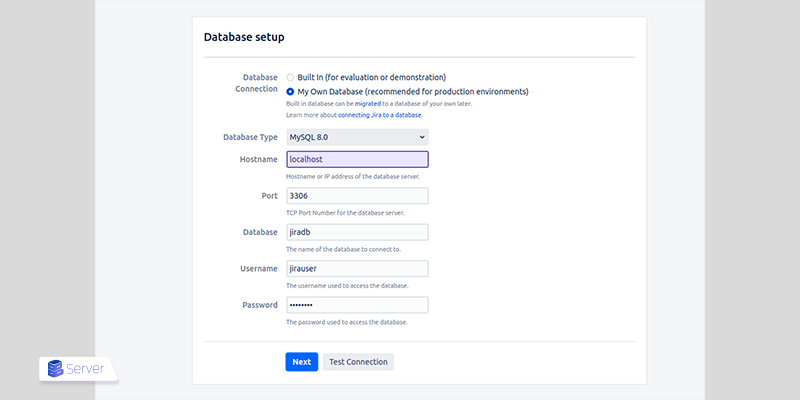
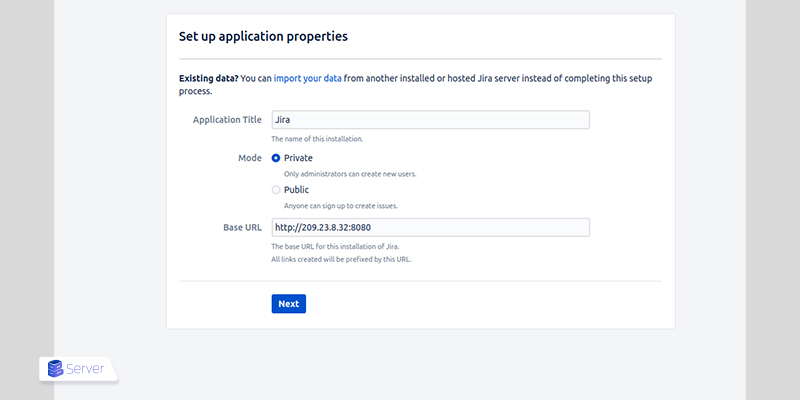
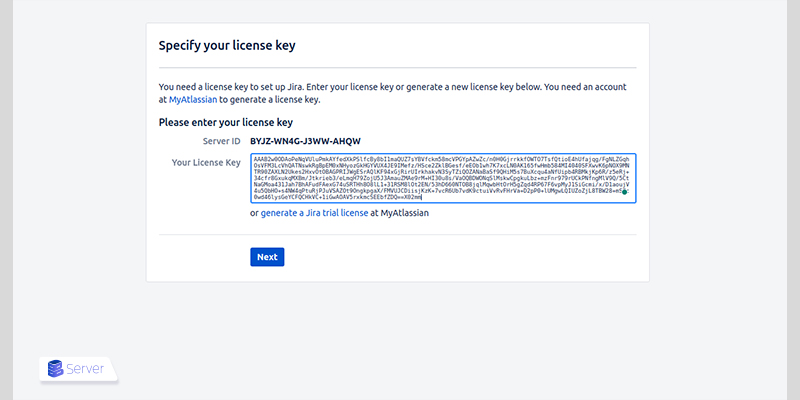
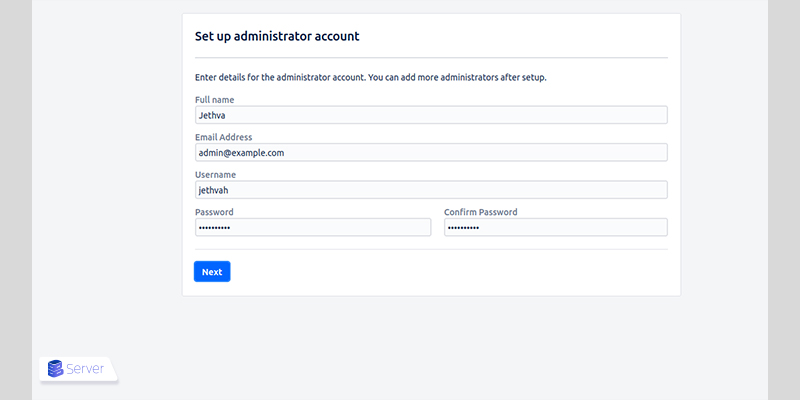
Step 4: Access the Jira Web Interface
Open Jira in your browser:
http://your-server-ip:8080
Initial setup includes:
- Database configuration
- Application settings
- Entering or generating a license
- Creating an admin account
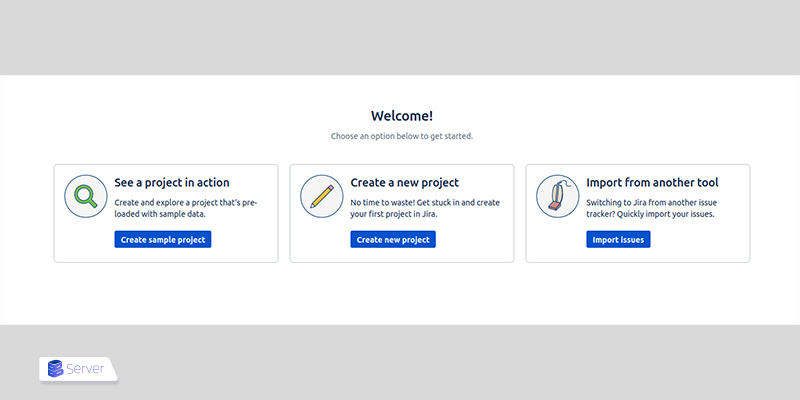
Creating a Project in Jira
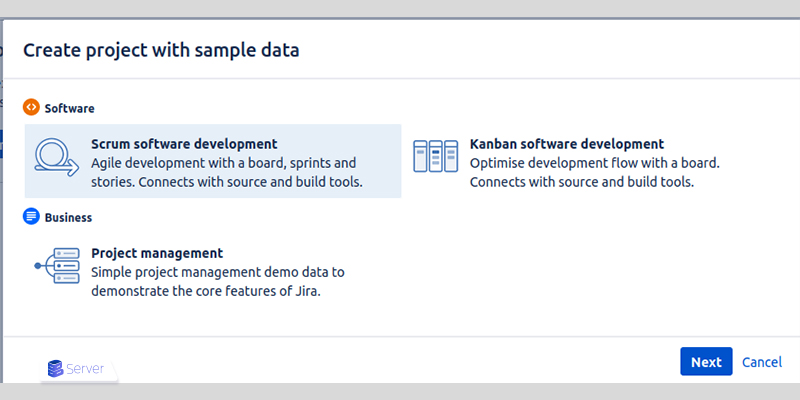
Once Jira is running, create a sample project:
- Click Create sample project.
- Select Scrum software development.
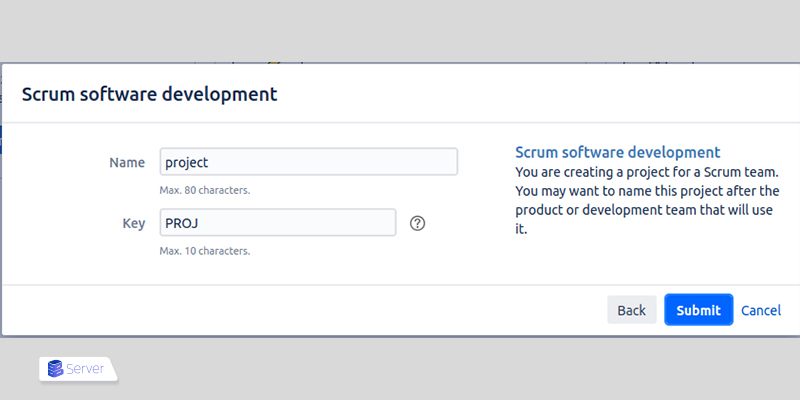
- Enter project name.
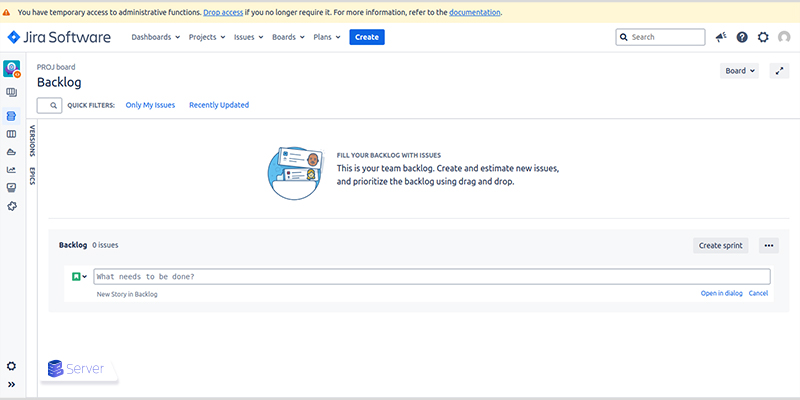
- Access the project dashboard.
You now have a functional Jira environment suitable for Agile workflows.
Installing Jira Add-ons
Add-ons (Marketplace Apps) enhance Jira capabilities.
1. Install Add-ons Online
- Go to Apps > Manage apps
- Click Find apps
- Search or browse categories
- Select Install, Free trial, or Buy now
- Enter the license key if required
2. Install Add-ons Offline
- Download .jar or .obr file
- Go to Apps > Manage apps > Upload app
- Upload or paste URL
- Enter signature hash if needed
Add-on License Activation
- Go to Manage apps
- Select add-on
- Enter License key
Conclusion
Jira is one of the most powerful platforms for managing projects, tracking tasks, supporting Agile methodologies, and enabling team collaboration. In this guide, you learned how to install Jira on a Linux server from scratch, including database configuration, driver setup, and web-based initialization. With flexibility, integrations, and extensive add-ons, Jira can be fully customized to fit your organization’s workflow.
FAQs
What is Jira?
Jira is a project management and issue-tracking platform developed by Atlassian, widely used across software and business teams.
What programming language is Jira built with?
Jira is primarily written in Java and uses Tomcat, OSGi, and relational databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Why use Jira plugins?
Plugins extend Jira functionality, enhance automation, allow integrations, and fill capability gaps.