In this tutorial, we will explore solutions to common connection problems encountered with both Windows and Linux VPS. Connection issues with servers can be particularly frustrating, especially when the server is being used for specific tasks. Even small problems can lead to significant time spent troubleshooting in an effort to maintain a stable and reliable connection. In this article, we’ll cover the most frequent VPS connection issues that may cause server downtime and provide solutions to help you resolve these disruptive problems. We will begin by discussing each connection issue in detail and then move on to secondary errors and their corresponding fixes.
Common Causes of VPS Connection Issues
VPS issues are not limited to RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) errors. Problems with RDP can lead to loss of server connections, but there are other secondary factors to consider. These include internet outages, disruptions caused by the service provider, issues with the provider’s infrastructure, or operating system malfunctions—all of which can result in connection loss.
Because of this, when purchasing a VPS, it’s crucial to focus not only on the features of the VPS itself but also on the reputation of the service provider. We recommend prioritizing factors like high uptime, adequate resources, robust support systems, and choosing a provider with a strong reputation. These steps can help reduce the risk of failure and minimize connection disruptions.
Windows VPS Connection Issues
It’s important to note that RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) functions the same across all versions of Windows Server. As a result, you may encounter the same errors when connecting to a Windows VPS. Additionally, there are times when, aside from the main issue, RDP connections can be disrupted due to secondary factors.
Below, we address the following common issues:
- The default RDP port
- Insufficient permissions
- Multiple users accessing RDP simultaneously
- Excessive bandwidth usage
1. Lack of Sufficient Permissions
Problem:
Occasionally, you may lose connection to a Windows server if you don’t have the necessary permissions to access it. This is especially common on Windows Server 2016.
Solution:
To resolve insufficient permissions:
- Open the Group Policy Object Editor.
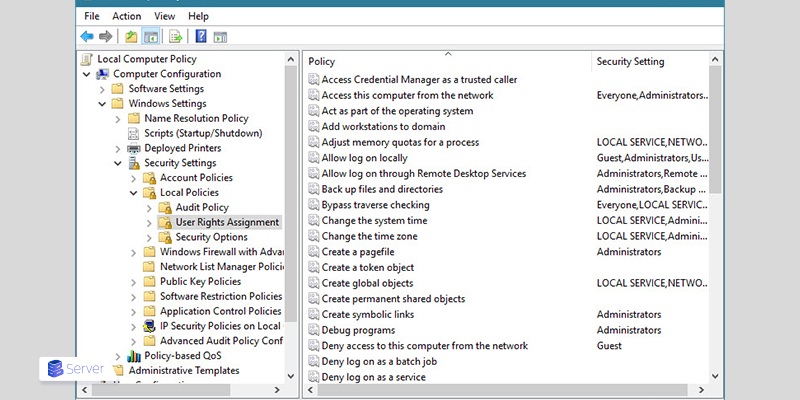
- Navigate to:
Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > User Rights Assignment - Locate and select “Allow logon through Remote Desktop Services”.
- Click Add required group, then click OK to apply changes.
Problem:
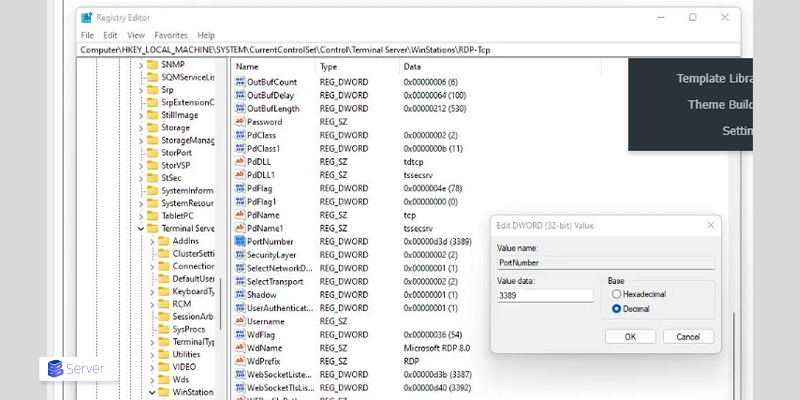
Connecting to a Windows server via a port other than the default RDP port (3389) may result in connection failure. This is often due to network firewalls restricting access to only port 3389.
Solution:
If using a non-default port, follow these steps to restore the default port:
- Open the Windows Registry Editor.
- Navigate to:
Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server\WinStations\RDP-Tcp - Locate the “Port Number” key, change the “Base” option to Decimal.
- Set the Value data to 3389 and restart the system for changes to take effect.
3. Multiple Users Accessing RDP Simultaneously
Problem:
If another user with a similar username is logged in, or if your server restricts simultaneous logins, you may encounter an error stating that another user is already connected. This can cause your session to drop.
Solution:
To address this:
- Navigate to:
All Programs > Administrative Tools > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration - Under the “Connections” section, enable “Restrict each user to a single session”.
If the issue persists, contact your VPS service provider for additional assistance.
4. Excessive Bandwidth Usage
Problem:
Excessive bandwidth consumption can slow down your RDP session or cause disconnects. This may happen if certain applications or graphics settings are using too much bandwidth.
Solution:
To optimize bandwidth:
- Close bandwidth-heavy applications on the server.
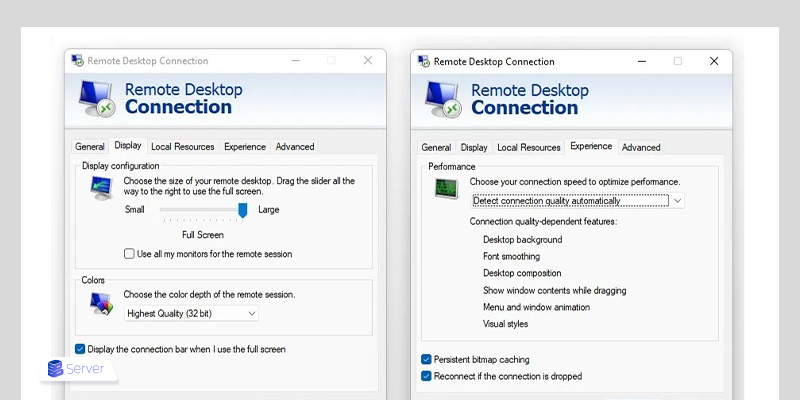
- Adjust the display resolution or reduce visual effects in the RDP settings:
-
- Go to the Experience and Display sections of RDP settings.
- Uncheck any unnecessary visual options (e.g., desktop background, font smoothing).
Linux VPS Connection Issues
If you’ve worked with Linux servers, you’re probably familiar with some of the reasons behind connection losses. However, the primary issue with connecting to a Linux VPS can stem from various factors. As mentioned earlier, secondary issues often affect RDP connections, but with Linux servers, many of these connection errors are related to the PuTTY application itself, which can lead to lost connections.
Below, we address some of these issues and their solutions:
- Blank screen when attempting to log in via SSH
- PuTTY Fatal Error: Line 11
- PuTTY Fatal Error: Multiple connection attempts
- PuTTY Connection Timed Out error
Now, let’s explore these connection errors in more detail and provide solutions to resolve them.
1. Blank Screen When Attempting to Log into SSH
Problem:
A blank screen may appear with the error:
"PuTTY Network Error: Software Caused Connection Cancellation."
This issue typically happens after PuTTY has been idle for a long period with no commands issued.
Solution:
1.Edit the sshd_config file as root:
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_confi
or
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
2.Locate ClientAliveInterval and set the value to 60.
3.Restart SSH:
For RHEL 5/6
service sshd restart
This ensures the server will maintain the connection for 60 seconds of inactivity before timing out.
2. PuTTY Fatal Error: Line 11
Problem:
You may see the following error:
"SSH requires agent forwarding to connect using a public key over TCP."
This usually occurs on Debian servers when public key authentication is not enabled, or the PuTTY agent is not configured for forwarding.
Solution:
- In PuTTY, go to:
Connection > SSH > Authentication - Enable “Allow Agent Forwarding”.
- Also, ensure that public key authentication is enabled for TCP:
- Open the TCP service configuration.
- Enable Public-Key Authentication if it’s disabled.
3. PuTTY Fatal Error: Multiple Connection Attempts
Problem:
This error happens when multiple quick connection attempts trigger security applications (like Fail2Ban or LFD) to block your IP, often due to failed login attempts.
Solution:
- Log in again after waiting for the block to clear.
- If your IP is still blocked, contact your provider to review firewall logs and reset login details.
4. PuTTY Connection Timed Out Error
Problem:
The connection may time out due to network issues (firewalls or routers), server problems (incorrect IP), or software misconfigurations.
Solution:
- In PuTTY, go to General Configuration.
- Under Connections, set KeepAlive in seconds to 20 and enable “Enable TCP Keepalives”.
This sends “null packets” every 20 seconds to keep the connection alive and reduce the likelihood of a timeout.
Summary
In this comprehensive tutorial, we explored both primary and secondary causes of connection issues with VPS and provided solutions to address them. From RDP errors on Windows to common problems with the PuTTY application on Linux, these issues can lead to server connection loss. Many of these problems can be prevented by properly configuring ports, permissions, managing bandwidth, and ensuring correct security settings. Additionally, selecting a reliable provider with strong support and sufficient resources is crucial for maintaining a stable and uninterrupted connection.
FAQs
1. Why is my VPS connection slow?
There can be multiple reasons for a slow VPS connection, including high bandwidth usage by certain applications, insufficient system resources, or network issues. To improve the connection, you can reduce the display resolution, close unnecessary applications, and ensure that your VPS provider offers adequate resources.
2. How can I fix a blank screen when connecting to SSH on Linux VPS?
This issue is often related to idle timeouts. You can resolve it by editing the sshd_config file to set the ClientAliveInterval to 60 seconds. This will prevent the server from disconnecting due to inactivity.
3. What should I do if my IP gets blocked while using SSH on a Linux server?
Security tools like Fail2Ban or LFD may block your IP if there are multiple failed login attempts. To resolve this, either wait for the block to be lifted or contact your service provider to unblock your IP and reset your login attempts.
4. How do I enable agent forwarding in PuTTY?
To enable agent forwarding in PuTTY, navigate to Connect > SSH > Authentication and check the Allow Agent Forwarding option. This allows SSH clients to forward authentication requests securely.
5. Why does my PuTTY session keep timing out?
The PuTTY session might time out due to network issues, incorrect settings, or inactivity. To fix this, you can configure TCP Keepalives in the PuTTY settings under Connections > Sending of null packets. Setting it to 20 seconds ensures the connection stays active.
6. What is the default RDP port, and why do I need to use it?
The default RDP port is 3389. If you use a different port, your connection might be blocked by a firewall or the server might not accept it. It’s important to ensure that the correct port is being used for RDP connections.
7. How can I allow only one user to access RDP at a time on my Windows VPS?
To restrict users to a single RDP session, go to All Programs > Administrative Tools > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration, and enable the option Restrict each user to a single session under the Connections section.
8. Why am I getting the error “PuTTY Fatal Error: Line 11”?
This error occurs when the public key authentication for SSH is not enabled or the PuTTY agent is not configured for agent forwarding. To fix this, enable public key authentication in the server’s TCP service and configure PuTTY to allow agent forwarding.