The question What is VDI has become increasingly important as businesses move away from traditional desktop environments and toward centralized digital workspaces. VDI stands for Virtual Desktop Infrastructure, a technology that allows desktop operating systems to run on centralized servers instead of local machines. Users access their desktops remotely through a network connection, often using thin clients, laptops, or even tablets.
Understanding what is VDI and how it works is essential for IT decision makers, startups, and enterprises that want scalable and secure remote access to desktops without sacrificing performance or control. If you are interested to know more about VDI read this article to the end.
What Is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure?
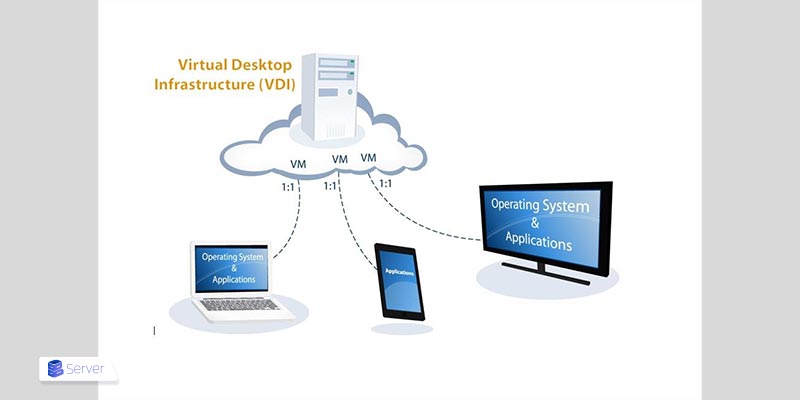
When people ask what is VDI desktop, they are usually referring to a virtualized desktop experience that behaves like a traditional computer but exists entirely within a server environment. Virtual desktop infrastructure separates the user interface from the physical hardware. The desktop environment runs on a centralized server, while the user interacts with it through a remote display protocol.
The most important thing about VDI you need to remember: The processing power, storage, and memory are all handled on the server side and this design allows IT teams to deploy standardized desktop environments quickly. Updates, patches, and software installations can be applied once and delivered instantly to all users.
This centralized model also reduces hardware dependency, since end users no longer need powerful local machines to run demanding applications.
Real Scenario of VDI in a Server
To understand what is VDI and how it works, imagine a pool of virtual machines running desktop operating systems such as Windows or Linux on a server. Each user connects to one of these virtual desktops through a secure network connection. Interactions between server and the user are in 4 steps:
- The server processes all computing tasks
- Only screen updates are transmitted to the user device
- Keyboard input is sent from the user to the server
- Mouse movements are relayed in real time between the user and the virtual desktop
Then a connection broker manages user authentication and assigns the correct virtual desktop to each user. Storage systems keep user data persistent, while hypervisors handle resource allocation. This architecture ensures that desktops can scale up or down based on demand without requiring physical intervention.
In real world deployments, VDI environments are often hosted on high performance servers or cloud platforms. Some businesses even deploy regional hosting solutions such as Germany vps to reduce latency for European users and ensure compliance with local data regulations.
Key Benefits of VDI Desktop Environments
While there are a lot of benefits lying in VDI and we could use it in different ways, the most important ones are explained below.
1. Centralized Security
One of the strongest advantages of a VDI desktop is centralized security. Since data never leaves the server, the risk of data loss caused by stolen, lost, or damaged devices is significantly reduced. Sensitive information remains within the controlled server environment, and access policies can be enforced consistently across all users, regardless of their location or device.
2. Operational Efficiency
Another major benefit is operational efficiency. IT teams can manage all desktops from a single centralized console, which dramatically reduces maintenance time and simplifies troubleshooting. Updates, patches, and configuration changes can be applied once and instantly reflected across multiple virtual desktops. Scaling is also much easier, as new users can be provisioned with fully functional virtual desktops in minutes rather than hours or days.
3. Cost Optimization
Cost optimization plays an important role in VDI adoption. Although the initial infrastructure investment can be significant, long term savings often come from reduced hardware requirements and lower support and maintenance overhead. End users no longer need high end local machines, and for organizations with distributed or remote teams, VDI removes the need to ship, replace, or manage physical desktops across multiple locations.
What is VDI Used For Across Industries
The question What is VDI used for has many answers depending on the industry:
- Healthcare: VDI enables secure access to patient records from multiple locations while helping organizations comply with strict data protection and privacy regulations.
- Finance: Financial institutions use VDI to create controlled and secure environments for handling sensitive transactions, financial data analysis, and regulatory compliance.
- Software Development: Development teams rely on VDI to build standardized, reproducible development environments that can be deployed instantly and maintained consistently across teams.
- Education: Educational institutions use VDI to give students access to specialized software and lab environments without requiring high-end or expensive personal hardware.
- Customer Support: Call centers and support teams benefit from VDI by allowing agents to log in from anywhere while maintaining uniform desktop configurations and security policies.
- Small Businesses: Small organizations adopt VDI to support remote work and centralized management without the complexity and cost of maintaining multiple physical systems.
VDI vs Traditional Desktops
Here is a helpful and comprehensive comparison covering all aspects:
| Aspect | Traditional Desktops | VDI Desktop Environments |
| Operating system location | The operating system is installed directly on a physical machine | The operating system runs centrally on a server |
| Data storage | User data is stored locally on the physical device | User data remains on the centralized server |
| Security | Higher risk of data loss due to device theft, damage, or loss | Reduced data loss risk since data never leaves the server |
| Scalability | Scaling requires purchasing and configuring new physical machines | New virtual desktops can be provisioned quickly from centralized resources |
| Maintenance | Updates and patches must be applied individually on each device | Updates and changes can be applied centrally and delivered to all users |
| Hardware failure impact | Hardware failures can cause downtime and potential data loss | If a device fails, the desktop remains accessible from another device |
| Remote and hybrid work | Limited flexibility and higher management complexity | High flexibility for secure access from multiple locations and devices |
Note: Scaling your project could start from a cheap vps hosting canada location and continue to a more powerful setup later.
Infrastructure Considerations For VDI Deployment
A successful VDI deployment depends heavily on the underlying infrastructure. Server performance, storage speed, and network latency all directly impact user experience. Choosing the right hosting environment is critical. Many organizations start with virtual private servers to test VDI workloads. For larger deployments, dedicated servers or high performance cloud infrastructure may be required.
Security is one of the primary reasons organizations adopt VDI. Centralized control allows administrators to enforce strict access policies, monitor activity, and isolate sensitive workloads. Data encryption, multi factor authentication, and role based access control are commonly integrated into VDI platforms. Compliance requirements are easier to meet when data resides in controlled environments. This is particularly important for industries subject to regulations such as GDPR or HIPAA.
The Future of VDI and Digital Workspaces
As cloud technologies evolve, VDI continues to integrate with broader digital workspace solutions. Automation, artificial intelligence driven resource allocation, and improved graphics virtualization are shaping the next generation of virtual desktops. The rise of remote work has accelerated interest in VDI as a long term solution rather than a temporary fix.
Organizations now view VDI as a strategic investment that supports flexibility, resilience, and scalability. Understanding What is VDI today means recognizing its role as a foundation for modern computing environments rather than just a remote desktop tool.
Conclusion
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure has transformed the way organizations deliver and manage desktop environments. By centralizing desktops on secure servers, VDI provides flexibility, security, and efficiency that traditional desktops struggle to match. From understanding what is VDI and how it works to exploring what is VDI used for across industries, it is clear that this technology is no longer optional for forward thinking organizations.
As infrastructure options expand and performance continues to improve, VDI is becoming more accessible to businesses of all sizes. Whether deployed on regional servers or cost effective VPS platforms, VDI represents a powerful step toward a more agile and secure digital future.