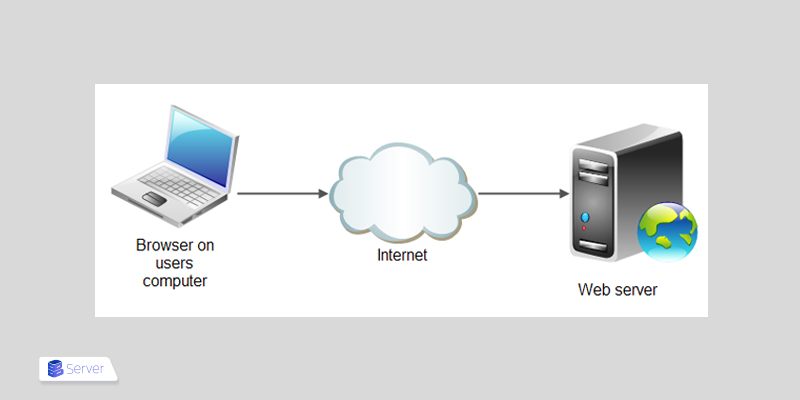
What is a Web Server? When you first became familiar with computer systems and internet browsers, you’ve probably wondered how these web pages are displayed to you. The answer is that a website is shown to you through a web server. When you request to view a site, your request is sent to a web server, and the desired pages are displayed to you.
In the following, we will dive deeper into the answer to the question “What is a web server?” and explore its features and applications.
Buyserver is one of the hosting service providers in the world, offering a wide range of servers. Different types of virtual servers, including Linux and Windows VPS, are provided to users with the best features and highest speeds.
What is a Web Server?
A web server consists of both hardware and software that use HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and other protocols to respond to client requests made over the World Wide Web. Simply put, a web server is a computer that stores, processes, and delivers various website files to users through web browsers.
The main task of a web server is to display website content by storing, processing, and serving web pages to users. In addition to HTTP, web servers also support SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) and FTP (File Transfer Protocol), which are used for email, file transfer, and storage.
The hardware of a web server is connected to the internet and helps establish communication between devices for data transfer. On the other hand, the web server software helps control user access to the hosted files. The web server process is an example of the client-server model. All systems and computers that host websites must use web server software.
Web servers are used in web hosting or data hosting for all websites, web-based applications, and web apps.
How Does a Web Server Work?
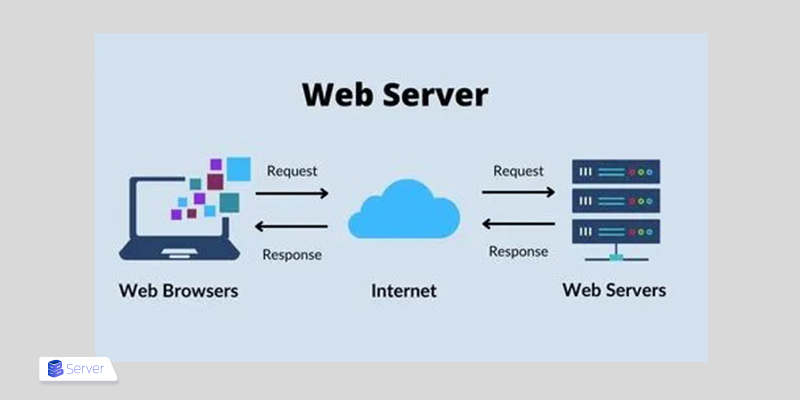
As explained in the definition of what a web server is, web servers follow the client-server model. In this structure, a program, known as the client, requests a resource or service from another program, the server.
To process client requests, web servers follow these steps:
- When a web user intends to access a website’s content, their web browser sends this access request over the internet. This request is called an HTTP request. The web browser resolves the IP address of the requested website through URL translation of web pages and the Domain Name System (DNS) or by searching its cache. This process finds the web server where the site files are hosted.
- The web server receives the HTTP request and processes it through its HTTP server. Once the HTTP server accepts the request, it searches the server’s files to retrieve the requested data.
- Then, the web server returns the site files to the web browser that sent the request. After that, the web user can view the website content.
However, if the HTTP server fails to find or process the requested files, it responds to the web browser with an error message. One of the most common error messages is a 404 error. In the case of permission issues, a 403 error may also appear.
On the other hand, if a web server cannot receive a timely response from another server acting as a proxy or gateway, a 504 error occurs.
What Are the Applications of a Web Server?
Web servers are used as part of other programs that operate with internet connectivity.
- Sending and receiving emails
- Requesting file downloads using the File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Creating and publishing web pages
In fact, web servers are hardware, software, or both working together to perform these tasks. Let’s explore the applications of a web server from two perspectives: hardware and software.
Hardware:
From a hardware perspective, a web server can be considered as a computer with software installed, where the website’s components such as documents, images, CSS style sheets, and others are stored. This hardware must be connected to the internet to facilitate data exchange.
Software:
From a software perspective, a web server is divided into several components that control user access to the website’s files hosted on the server. The server becomes accessible through the domain name of the websites stored on it.
Features of a Web Server
After reviewing what a web server is, let’s examine its features. In addition to supporting HTTP protocols to process incoming requests and responses, most web servers offer the following standard features:
Log Files:
Web servers document event or activity logs, such as requests, security files, and error reports generated by the server. Every time a web server receives a new request, a line of text is added to the log file.
Authentication:
Many servers provide this feature to control partial or full access to website resources. These features often include permission grants, which are issued when a password and username are entered.
Bandwidth Limiting:
Bandwidth on a web server refers to the amount of data the server can transmit or process in a given time. Limiting bandwidth controls response speeds to ensure the network isn’t overwhelmed and can deliver files properly.
Storage Space:
Storage space refers to the disk space available for storing files, which determines whether a web server can host a website.
Why Do We Use a Web Server?
As mentioned, web servers serve three main purposes:
- They host multiple websites or web applications.
- They process File Transfer Protocol (FTP) requests.
- Web servers are responsible sending and receiving emails.
Web servers host websites so that they can be accessed via the internet. This is why the features and functions of a web server are focused on creating and maintaining a hosting environment.
If you want to create and publish a website, you need access to a web server. The easiest way to do this is through web hosting services. Web hosting is a service that provides space on a server to store your website’s files and databases.
Another important role of a web hosting provider is ensuring the seamless operation of the servers. This includes tasks such as performing backups, caching, monitoring security, and general website maintenance. That’s why choosing a reliable hosting provider is crucial.
A web server that hosts your website should offer the following features:
- Uptime and Optimal Performance: A good web host maintains hardware and updates software, which helps improve website performance and keep it up to date.
- Secure Servers: Web hosting providers use effective security protocols to reduce vulnerabilities and protect hosted websites from malware or cyberattacks.
- Various Hosting Plan Options: Website owners can choose a hosting plan with different features and performance levels based on their needs.
- Cost-Effective: Website owners don’t need to maintain a dedicated server. Instead, they can choose a hosting plan that provides the necessary server resources, reducing costs.
- Flexibility: Web hosts offer scalable plans, allowing website owners to acquire additional hosting resources like storage or bandwidth as needed.
Static vs. Dynamic Web Servers
Web servers can deliver either static or dynamic content.
A static web server consists of a computer and HTTP software. Static web servers send website files to a web browser without making any changes to them.
A dynamic web server is made up of a static web server along with additional software. This additional software usually includes an application server and a database. Dynamic web servers essentially update the hosted files before delivering them through the HTTP server. This allows them to generate and deliver dynamic content to a web browser.
Best Web Server Software
Some of the most popular examples of web servers include:
Apache
Apache is a free and open-source web server that is used for many operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X. Since its introduction, Apache has become the best and most popular HTTP server. It is the oldest web server software and one of the most commonly used by website owners, developers, and hosting providers. The open-source nature of this web server has led programmers to constantly add various modules, and over the years, it has been continuously optimized. Apache holds more than a 31% market share.
NGINX
NGINX is a well-known open-source web server that initially only served HTTP web services. It is now also used as a reverse proxy, HTTP load balancer, and email proxy. NGINX is known for its speed and ability to handle multiple connections efficiently, which is why many high-traffic websites rely on its services.
Internet Information Services (IIS)
IIS is a highly flexible web server software widely used by Microsoft in Windows operating systems. This web server supports various frameworks, such as .NET and PHP-based frameworks.
Lighttpd
Lighttpd is a free and open-source web server that quickly became popular due to its low CPU usage. It is also well-known for its small memory footprint. This web server, being open-source, is ideal for environments with speed limitations. The key feature of Lighttpd is its ability to handle high volumes of concurrent requests efficiently.
Tips for Enhancing Web Server Security
There are many security measures that individuals can implement to create a safer web server experience. Some examples of security practices include processes such as:
- Reverse Proxy: Designed to hide an internal server, it acts as an intermediary for traffic originating from an internal server.
- Access Restrictions: Implementing processes such as restricting web host access to infrastructure machines or using Secure Socket Shell (SSH).
- Keeping Web Servers Updated: Ensuring that web servers are up to date to prevent exposure to any risks or vulnerabilities.
- Network Monitoring: Ensuring no unauthorized activity or threats are present on the network.
- Using Firewalls and SSL: A firewall can monitor HTTP traffic, while having a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) can help protect data security.
Conclusion
Web servers are offered with various features for different types of websites. Hosting service providers use these capabilities to provide you with the best options based on your needs. When you visit the websites of hosting companies, you’ll notice that they offer various plans with diverse features, allowing individuals to choose the best option based on the type of site, number of users, and other factors.